Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Ibaraki University*
JAEA-Review 2019-041, 71 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, has been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") since FY2018. The Project aims at solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence has been collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development have been promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Contribution to Risk Reduction in Decommissioning Works by the Elucidation of Basic Property of Radioactive Microparticles". In order to establish the decommissioning procedures (recovery of the melted fuels, decontamination inside the reactors, ensuring the safety of the workers, etc.) of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, radioactive microparticles released by the accident are an important information source for clarifying what had happened inside the reactors in the course of the accident. The purpose of the present study is to obtain detailed knowledge on the basic properties (particle size, composition, electrical/optical properties, etc.) of the radioactive microparticles, as well as to further elucidate the various properties of the radioactive microparticles including the quantitative evaluation of alpha-ray-emitters, through the Japan-UK synergetic research. Thus, we are conducting research and development that will contribute to the comprehensive works towards the risk reduction in the "decommissioning" plan.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Watanabe, Kazuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 43(4), p.305 - 310, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)We are developing an resonance ionization spectrometric apparatus aiming at an analysis of a radioactive isotope of calcium ( Ca) in nuclear waste materials. The developed system consists of the reference laser whose frequency was locked on a Doppler-free absorption line of 85Rb and the computer-controlled fringe offset lock system which transfer frequency stability of the reference laser to slave lasers for Ca excitation. With heterodyne spectroscopy and laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca, it was confirmed that the developed apparatus was suitable for resonance ionization spectrometric analysis.
Ca) in nuclear waste materials. The developed system consists of the reference laser whose frequency was locked on a Doppler-free absorption line of 85Rb and the computer-controlled fringe offset lock system which transfer frequency stability of the reference laser to slave lasers for Ca excitation. With heterodyne spectroscopy and laser induced fluorescence spectroscopy of Ca, it was confirmed that the developed apparatus was suitable for resonance ionization spectrometric analysis.
Iguchi, Kazunari; Esaka, Konomi; Lee, C. G.; Inagawa, Jun; Esaka, Fumitaka; Onodera, Takashi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Suzuki, Daisuke; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.363 - 366, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.86(Nuclear Science & Technology)In particle analysis for safeguards environmental samples, the fission track technique is very important to detect sub-micrometer particles containing uranium. In the technique the authors developed, the particles were recovered onto the polycarbonate membrane filter. The filter was dissolved in solvent and dried to form a thin film of detector, in which the particles were confined. After thermal neutron irradiation and etching, the particles of interest in the detector were easily identified with fission tracks, and were picked up for isotope ratio analysis. It was found, however, that the particles in the vicinity of the detector surface may fall off during the etching process. Therefore, optimization of the etching condition is required. In this work, the effects of etching time and enrichment of uranium in particles were investigated. Preliminary results suggest that etching time should be shorter with the increase in the enrichment.
Sakurai, Satoshi; Magara, Masaaki; Usuda, Shigekazu; Watanabe, Kazuo; Esaka, Fumitaka; Hirayama, Fumio; Lee, C. G.; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Kono, Nobuaki; Inagawa, Jun; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
no abstracts in English
Committee for the Joint Research Project on the Advanced Radiation Technology; Committee for the Collaborative Research on the Advanced Radiation Technology
JAERI-Conf 2000-008, 113 Pages, 2000/06
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Kenji; *; Ohira, Shigeru; Naruse, Yuji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 28(6), p.509 - 516, 1991/06
no abstracts in English

 Cr
CrShin, Sumio*; ; *; Nishida, Hiroshi*; ; ; Motoki, Ryozo
Igaku No Ayumi, 130(6-7), p.437 - 439, 1984/00
no abstracts in English
;
Anal. Chem., 55(13), p.2059 - 2062, 1983/00
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:61.91(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
*; *; *; *; ; ; ;
JAERI-M 9901, 14 Pages, 1982/01
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Hajimu; Kokubu, Yoko; Umeda, Koji
no journal, ,
JAEA installed an IsotopX NGX noble gas mass spectrometer with an water sample oriented preparation system in Tono Geoscience Center to measure helium accumulation age and neon isotope ratio of ground water for estimation of ground water stability on long term geological stability survay on geological disposal of nuclear waste. High precision isotope analysis by multi-collector mass spectrometer is neccessary tool for neon isotope analysis of young ground water due to small isotopic variation of neon for nucleogenic reaction or mixing of volcanic fluids in ground water. NGX-004 was configured for simultanous measurement of neon isotopes with 2 faradays for  Ne and
Ne and  Ne, and 1 SEM for
Ne, and 1 SEM for  Ne spaced out 1 m/z each other. 10.084
Ne spaced out 1 m/z each other. 10.084  0.002 of
0.002 of  Ne/
Ne/ Ne and 0.02598
Ne and 0.02598  0.00004 of
0.00004 of  Ne/
Ne/ Ne were obtained by
Ne were obtained by 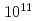 ohm faraday and
ohm faraday and 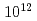 ohm faraday, and ion count and
ohm faraday, and ion count and 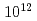 ohm faraday, which is able to resolve 0.2% difference.
ohm faraday, which is able to resolve 0.2% difference.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Oba, Masaki; Ito, Chikara; Kato, Masaaki
no journal, ,
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) for elemental analysis and Laser Ablation Resonance Absorption Spectroscopy (LARAS) for isotope analysis have been developed as an analytical technique for Low-decontaminated MOX fuel with fissionable Miner Actinide elements (MA) and as for one of the diagnostic tool of nuclear fuel debris and polluted materials in the decommissioning of the severe accident nuclear power station. Specialized glove box with auto and remote arraignment system for LIBS and LARAS was constructed, and the detection limit of Pu in MOX to be several 1000 ppm and some hyper fine structures of  Pu were demonstrated. For the diagnostic tool in the decommissioning of damaged core, optical fiber based portable LIBS probe made by radiation resistant optical fiber is under construction, and just now, some specific spectra from the simulated sample of molten debris made by sintered oxide of Zr and U is successfully observed under water condition or strong radiation field.
Pu were demonstrated. For the diagnostic tool in the decommissioning of damaged core, optical fiber based portable LIBS probe made by radiation resistant optical fiber is under construction, and just now, some specific spectra from the simulated sample of molten debris made by sintered oxide of Zr and U is successfully observed under water condition or strong radiation field.